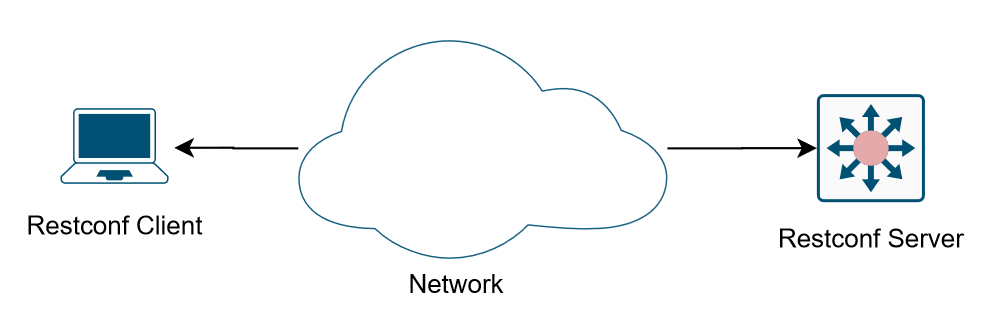
Understanding RESTCONF
Basic Concepts of RESTCONF
- Derived from Netconf
- Model definition in YANG
- The request/response data is XML or JSON
- Using HTTPS methods(GET / PATCH / POST / DELETE / PUT)
- RESTCONF URI format: /<api-entry>/<resource-type>/<yang-module:resource>
Yang model
Enabling RESTCONF on IOS-XE
haifeli-C9800#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. haifeli-C9800(config)#restconf haifeli-C9800(config)#ip http secure-server haifeli-C9800(config)#end haifeli-C9800#wr Building configuration... [OK] haifeli-C9800#
PYANG
pyang is a YANG validator, transformator and code generator, written in python. It can be used to validate YANG modules for correctness, to transform YANG modules into other formats, and to generate code from the modules.
Installation
It is recommended to use pyang in a linux environment.
pip install pyang
Tree output
The command is as follows.
pyang -f tree <filename>
Example:
root@yang-explorer-1:/cisco/xe/1731# pyang -f tree Cisco-IOS-XE-memory-oper.yang module: Cisco-IOS-XE-memory-oper +--ro memory-statistics | +--ro memory-statistic* [name] | +--ro name string | +--ro total-memory? uint64 | +--ro used-memory? uint64 | +--ro free-memory? uint64 | +--ro lowest-usage? uint64 | +--ro highest-usage? uint64 +--rw schema-metadata-Cisco-IOS-XE-memory-oper | +--rw json-metadata-leaf? empty +--rw gnmi-model-data root@yang-explorer-1:/cisco/xe/1731#
Curl
The command is as follows.
curl -k -u username:password <link>
Example:
C:\Users\test>curl -k -u admin:Cisco123 https://10.106.63.111/restconf/data/Cisco-IOS-XE-native:native/interface/Vlan=62/ip/address/primary <primary xmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XE-native" xmlns:ios="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XE-native"> <address>10.106.62.111</address> <mask>255.255.255.0</mask> </primary> C:\Users\test>
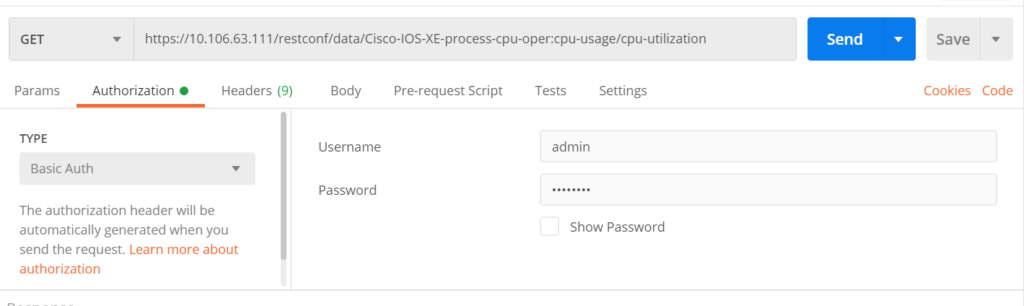
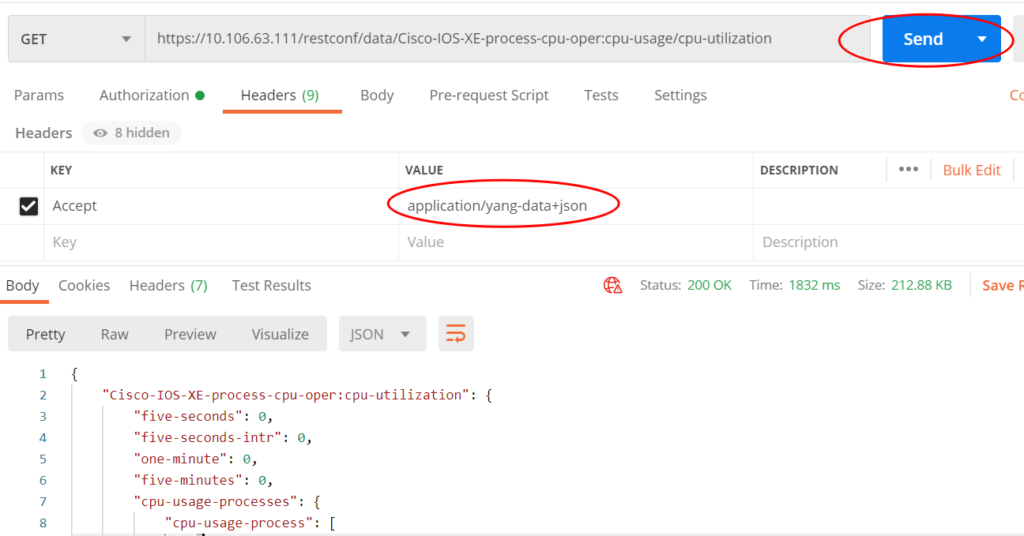
Postman
Postman is a powerful API debugging tool that we can use to send HTTP requests.
Python script
Usually using the requests module to send HTTP requests.
import requests
requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings()
host = '10.106.53.53'
user = 'admin'
password = 'Cisco123'
url = "https://{h}/restconf/data/Cisco-IOS-XE-process-cpu-oper:cpu-usage/cpu-utilization".format(
h=host)
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/yang-data+json',
'Accept': 'application/yang-data+json'}
response = requests.request(
"GET",
url,
auth=(
user,
password),
headers=headers,
verify=False)
print(response.json()[
'Cisco-IOS-XE-process-cpu-oper:cpu-utilization']['one-minute'])
Axios
If we are developing a web application, we can use axios to send HTTP requests.
Installation
Using npm
npm install axios
Using unpkg CDN
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
Example
The following is an Vue.js example.
<script>
axios.defaults.withCredentials = true;
const url =
"https://10.106.53.53/restconf/data/Cisco-IOS-XE-process-cpu-oper:cpu-usage/cpu-utilization/five-seconds";
const config = {
data: {},
headers: {
Accept: "application/yang-data+json",
},
};
export default {
data() {
return {
cpuUsage: [],
};
},
methods: {
getData: function () {
axios.get(url, config).then((response) => {
console.log(
response["data"]["Cisco-IOS-XE-process-cpu-oper:five-seconds"]
);
this.cpuUsage.push(
response["data"]["Cisco-IOS-XE-process-cpu-oper:five-seconds"]
);
});
},
},
computed: {
results() {
return this.cpuUsage;
},
},
};
</script>References
RESTCONF Protocol
Introduction to RESTCONF
RESTCONF Configuration
1 Response
[…] Understanding RESTCONF: https://lihaifeng.net/?p=922#Enabling_RESTCONF_on_IOS-XE […]